Consider a system of particles 1,2,...,n. Their total mass is:
Their total momentum is:
Define the center-of-mass coordinate vector:
The x-coordinate of the center of mass is, for example:
Why is this useful?
We can find the equation of motion for the center of mass by taking two time derivatives and multiplying with M => Newton's Second Law for a system of particles:
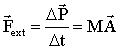
Note that only the net external force enters here. The internal forces between the particles pairwise add up to 0 because of Newton's Third Law.
Consequences: