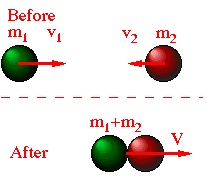
 In
this limit, the colliding partners stick together:
In
this limit, the colliding partners stick together:This is the other limit of collisions that we can perform calculations for. We have already briefly touched on this result, but here we explicitly will give the general answer.
 In
this limit, the colliding partners stick together:
In
this limit, the colliding partners stick together:
From momentum conservation, we then get:
Solving this for the velocity ![]() yields then:
yields then:
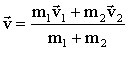
This result is valid for any number of spatial dimensions. Note that there is a whole class of collisions which are inelastic but not totally inelastic.