
 Question:
Question:
 Question:
Question:
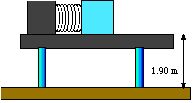
A block of ice with mass 0.120 kg is placed against a horizontal compressed spring mounted on a horizontal tabletop that is 1.90 m above the floor. The spring has a spring constant of 2940 N/m and is initially compressed 0.045 m. The spring is released and the block slides along the table, goes off the edge, and travels to the floor. If there is no friction, what is the speed of the block of ice when it reaches the floor?
Answer:
Again we could try and solve for the trajectory, but energy considerations make life a lot easier. Initially, the block has no kinetic energy, and all energy is potential energy; finally, the block has only kinetic energy.
[initial] E0 = Uspring + Ugravity + K = k x2 + m g h + 0 [final] E = 0 + 0 +
m v2 E = E0 =>
mv2 =
k x2 + m g h
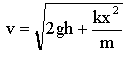
= 9.32 m/s