
From the results on the previous page we can obtain the radius of the nth orbit by substituting the classical expression for v2 with Z =1 into the Bohr quantum model
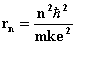
where k = 9.0 x 109 N-m2/C2.
We can rewrite this formula as rn = n2ao where
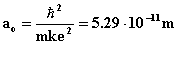
which is called the Bohr radius.
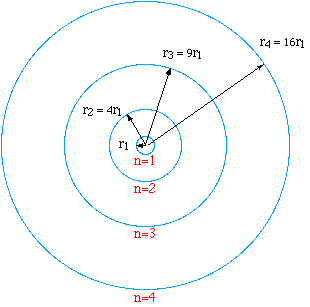
In the drawing to the right, the first four orbits are drawn to
scale. The orbit corresponding to n = 1 has the radius r1
= ao. The electron may not reside in any orbit between
these orbits. The radii are quantized meaning that when the electron
is in one of these orbits, it does not radiate.
© MultiMedia Physics 2000