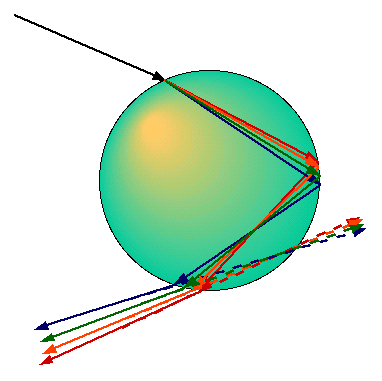

The index of refraction of a material is not a constant but usually is dependent on the frequency and wavelength. This results in (slightly) different deflection angles for different wavelengths when light passes from one medium another. This effect is called dispersion.
The most commonly known examples of dispersion are found in prisms
and rainbows. In the figure above, we schematically show the
refraction and reflection of sunlight on water droplets, giving rise
to rainbows. The average angle between incoming and reflected light
is 41
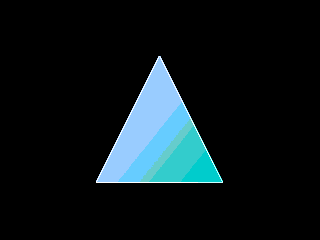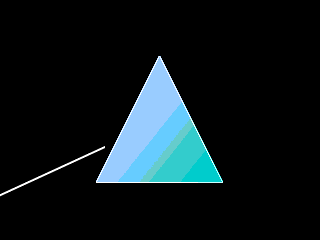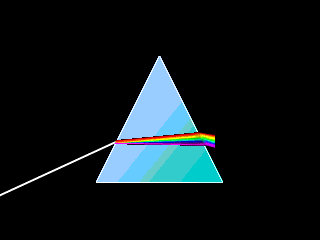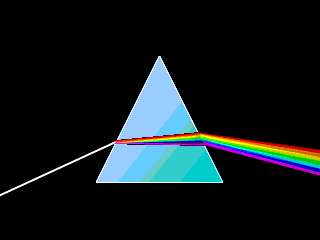
Another example for dispersion is the refraction of light by a prism, as shown below:
© MultiMedia Physics 2000