|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definition:
The equivalent capacitance is the value of one capacitor which, when replacing the two capacitors, will draw the same charge from the battery as the two (or more than two) original capacitors.
Capacitors can be connected in two basic ways, in series or in parallel. And the good news is that we can calculate how to combine two capacitors in both ways and how to find the equivalent capacitance.
Furthermore, it will turn out to be possible to successively reduce very complicated combinations of capacitors to find the equivalent capacitance using the rules for the two elementary parallel and series cases.
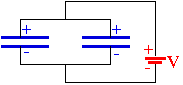
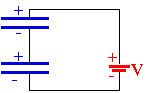
The pictures on the right contain these most simple arrangements of capacitors in circuits. Right now these circuits only contain the capacitors, indicated by the symbol of two parallel lines of equal length (in blue here), and the source of the potential drop in the circuit (parallel lines of unequal length). Later in this class, we will learn that these are batteries or external voltage supplies. The black lines connecting the elements have no real properties, except that they can conduct electricity without any loss. We may think of these as the wires connecting circuit elements.
© MultiMedia Physics 2000